| KCNQ1基因多态性与高尿酸血症的关联研究 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 孙凯琳 王毅鹏 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.昆明医科大学附属延安医院 内分泌科,云南 昆明 650051;2.昆明市延安医院 体检中心,云南 昆明 650051 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 云南省卫生和计划生育委员会医学学科带头人培养计划(No:D-2017042) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 
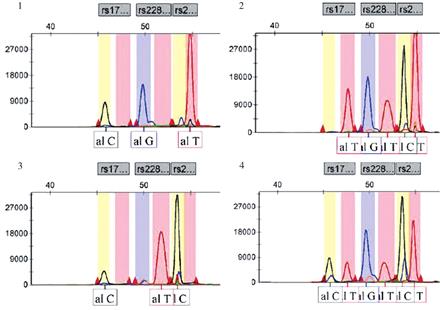
目的 探讨KCNQ1基因多态性与高尿酸血症发病的关联。方法 采用病例-对照研究和SNaPshot测序技术,对120例高尿酸血症患者(高尿酸血症组)和180例健康对照者(对照组)KCNQ1基因rs179785、rs2283228及rs2237892位点多态性进行分型,并结合其临床资料、生化指标进行关联分析。结果 与对照组比较,高尿酸血症组体重指数(BMI)、收缩压、舒张压、丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT)、天门冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)、甘油三酯(TG)、尿素、肌酐(Cr)和尿酸(UA)水平较高(P <0.05),而高密度脂蛋白(HDL)水平较低(P <0.05);两组的葡萄糖(Glu)、总胆固醇(TC)、低密度脂蛋白(LDL)水平比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。两组rs2283228、rs2237892位点基因型分布频率比较,差异均有统计学意义(P <0.05);与对照组比较,高尿酸血症组rs2283228位点AC基因型比例较高(P <0.017),而rs2283228位点CC基因型和rs2237892位点TT基因型比例较低(P <0.017);两组rs179785位点基因型分布及3个位点等位基因频率比较,差异无统计学意义(P >0.05)。无论是否调整混杂因素,rs2283228位点AC基因型均会增加高尿酸血症的发病风险,调整后[R=4.027(95% CI:1.411,11.492),P <0.05];rs2237892位点CT、TT基因型和T等位基因均会降低其发病风险,调整后[R=0.263(95% CI:0.094,0.738),P <0.05]、[R=0.125(95% CI:0.024,0.647),P <0.05]、[R=0.309(95% CI:0.147,0.652),P <0.05]。而rs179785位点多态性与高尿酸血症的关联无统计学意义(P >0.05)。结论 KCNQ1基因rs2283228位点AC基因型可能为高尿酸血症发病的危险因素,rs2237892位点CT、TT基因型和T等位基因可能为其发病的保护因素。
|
| 关 键 词: | 高尿酸血症 KCNQ1基因 多态性 SNaPshot测序 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-10-15 |
|
| 点击此处可从《中国现代医学杂志》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中国现代医学杂志》下载全文 |
|


