| 摘 要: | 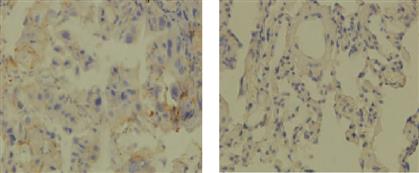
目的 探讨范科尼贫血D2蛋白(FANCD2)、乳腺癌易感基因2定位协作蛋白(PALB2)表达水平与非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)临床特征及预后的关系。方法 选取2017年11月—2019年10月成都市第二人民医院收治的194例NSCLC患者作为研究对象。将手术过程中取得癌组织标本作为NSCLC组,将对应的癌旁组织标本作为癌旁组,每组194例。采用免疫组织化学法检测FANCD2、PALB2在NSCLC患者癌组织及癌旁组织中的表达情况;分析FANCD2、PALB2表达与NSCLC患者临床病理特征的关系;采用Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,采用Cox比例风险模型分析探讨NSCLC患者预后的影响因素。结果 NSCLC组FANCD2、PALB2阳性率高于癌旁组(P <0.05)。Spearman相关性分析显示,NSCLC患者癌组织中FANCD2蛋白与PALB2蛋白呈正相关(rs =0.486,P <0.05)。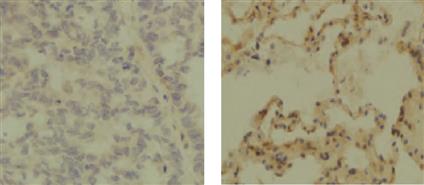
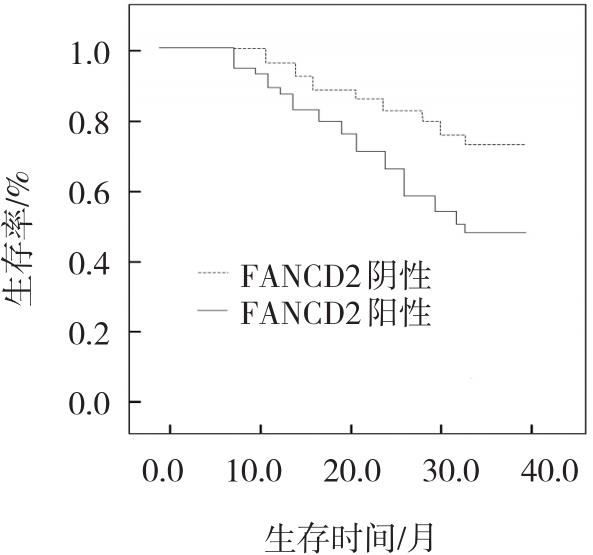
不同年龄、性别、吸烟、组织学分型、肿瘤直径患者FANCD2、PALB2阳性率比较,差异均无统计学意义(P >0.05)。TNM分期为Ⅲ、Ⅳ期,低分化,有淋巴结转移患者高于TNM分期为I、Ⅱ期,中/高分化,无淋巴结转移患者(P <0.05)。多因素逐步Cox回归分析结果显示:TNM分期Ⅲ、Ⅳ期[H^R=4.125,(95% CI:2.187,10.035)]、低分化[H^R=3.146,(95% CI:3.115,9.264)]、淋巴结转移[H^R=4.124,(95% CI:3.005,13.145)]、FANCD2阳性[H^R=5.146,(95% CI:3.784,12.689)]、PALB2阳性[H^R=4.563,(95% CI:2.845,7.398)]是NSCLC患者复发的影响因素(P <0.05)。多因素逐步Cox回归分析结果显示,TNM分期Ⅲ/Ⅳ期[H^R=3.689,(95% CI:2.963,11.254)]、低分化[H^R=2.167,(95% CI:1.998,5.996)]、淋巴结转移[H^R=5.648,(95% CI:3.552,12.953)]、FANCD2阳性[H^R=3.886,(95% CI:2.958,12.775)]、PALB2阳性[H^R=4.633,(95% CI:1.968,11.547)]是NSCLC患者预后的影响因素(P <0.05)。FANCD2阳性患者与阴性患者生存率比较,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05);PALB2阳性患者与阴性患者的生存率比较,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05)。结论 FANCD2、PALB2在NSCLC患者癌组织中呈高表达,与TNM分期、分化程度、淋巴结转移密切相关,可作为辅助评估患者预后和复发的潜在标志物。
|



