| 超声造影结合定量分析法及血清TSH、Gal-3、CK-19诊断甲状腺微小乳头状癌的临床价值 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 韩云霞 李雪梅 欧阳向柳 张春英 郑立春 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.唐山市工人医院,超声医学科,河北 唐山 063000;2.唐山市工人医院,病理科,河北 唐山 063000;3.唐山市工人医院,头颈外科,河北 唐山 063000;4.唐山市工人医院,核医学科,河北 唐山 063000 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 河北省自然科学基金(No:H2020209193);河北省医学科学研究课题(No:20201517) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 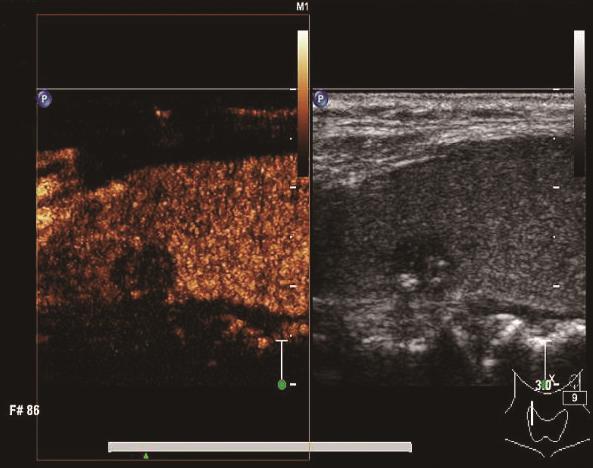
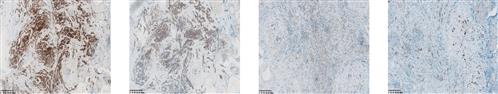
目的 探讨超声造影(CEUS)结合定量分析法及血清促甲状腺激素(TSH)、半乳糖凝集素3(Gal-3)、细胞角蛋白(CK-19)诊断甲状腺微小乳头状癌(PTMC)的临床价值。方法 回顾性分析2019年4月—2022年4月于唐山市工人医院行手术治疗的128例甲状腺微小结节患者的临床资料,其中59例PTMC患者作为PTMC组,69例甲状腺肿伴乳头状增生患者作为良性组。两组患者入院后均接受CEUS检查,以化学发光免疫法检测血清TSH,以免疫组织化学SP法检测Gal-3、CK-19表达。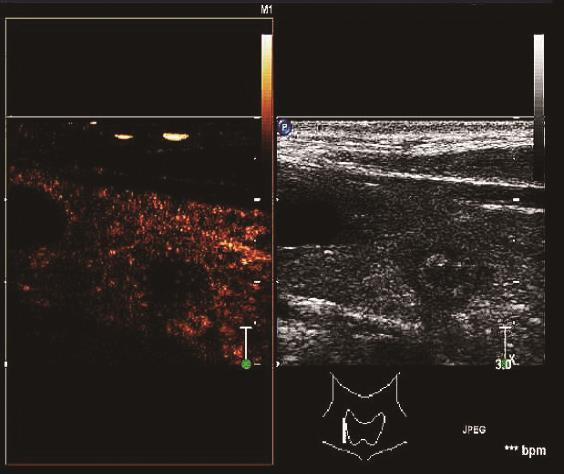
比较两组CEUS特征(增强顺序、消退模式、增强模式、环形增强、达峰强度、均匀增强)及参数[灌注峰值(Peak)、达峰时间(TP)、灌注率(Shapness)、曲线下面积(AUC)],比较两组血清TSH水平与Gal-3、CK19表达情况,通过受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线分析CEUS参数及血清TSH水平诊断PTMC的价值。最后以临床诊断结果为金标准,通过一致性分析Gal-3、CK-19单独及CEUS参数、TSH、Gal-3、CK-19联合诊断PTMC的效能。结果 PTMC组增强顺序向心性、消退模式快出、增强模式慢进...
|
| 关 键 词: | 甲状腺微小乳头状癌 甲状腺微小结节 超声造影 促甲状腺激素 半乳糖凝集素3 细胞角蛋白 诊断 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-01-17 |
|
| 点击此处可从《中国现代医学杂志》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中国现代医学杂志》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|



