| 母子关系在母亲养育压力与学龄前儿童情绪行为问题关联中的作用 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 何海燕 余敏 宁曼 崔晓晨 贾丽媛 李若瑜 万宇辉 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.芜湖市妇幼保健计划生育服务中心(芜湖市妇幼保健院),安徽芜湖 241000;2.安徽医科大学公共卫生学院儿少卫生与妇幼保健学系/出生人口健康教育部重点实验室/ 人口健康与优生安徽省重点实验室,安徽合肥 230032 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 国家自然科学基金(82273652);安徽省自然科学基金(2208085Y23)。 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 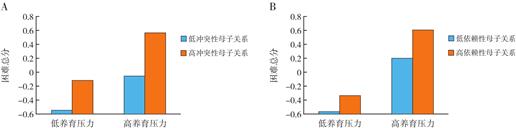
Objective To study the moderating effect of mother-child relationship in the association between maternal parenting stress and emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children, and to provide reference for the prevention and control of emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children. Methods Using a stratified cluster sampling method, 2 049 preschool children were surveyed from November to December 2021, who sampled from 12 kindergartens in Wuhu City, Anhui Province. The emotional and behavioral problems of preschool children were assessed with the Strength and Difficulties Questionnaire. Pearson correlation analysis was used to evaluate the relationship of maternal parenting stress and mother-child relationship with children's emotional and behavioral problems. The PROCESS Macro was used to analyze the moderating effect of conflicted and dependent mother-child relationships in the association between maternal parenting stress and emotional and behavioral problems in these preschool children. Results Among these preschool children, maternal parenting stress was positively correlated with the scores of emotional symptoms, conduct problems, hyperactivity, and peer problems subscales and total difficulty scores (P<0.001); intimate mother-child relationships were negatively correlated with the scores of conduct problems, hyperactivity, and peer problems subscales and total difficulty scores (P<0.001); conflicted and dependent mother-child relationships were positively correlated with the scores of emotional symptoms, conduct problems, hyperactivity, and peer problems subscales and total difficulty scores (P<0.001). After controlling for relevant confounding factors, conflicted mother-child relationship (β=0.05, P=0.001) and dependent mother-child relationship (β=0.04, P=0.012) were found to have a moderating effect on the association between maternal parenting stress and total difficulty scores in these preschool children. Conclusions Negative mother-child relationships play a moderating role in the association between maternal parenting stress and emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children. Prevention of emotional and behavioral problems in preschool children should focus on reducing maternal parenting stress and improving negative mother-child relationships. © 2023 Xiangya Hospital of CSU. All rights reserved.
|
| 关 键 词: | 情绪行为问题 养育压力 母子关系 调节效应 学龄前儿童 |
| 收稿时间: | 2022-10-12 |
| 本文献已被 维普 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《中国当代儿科杂志》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中国当代儿科杂志》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|

