| 手助腹腔镜与开放手术活体供肾取肾术的系统评估 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 李涛, 付生军, 董治龙, 等. 手助腹腔镜与开放手术活体供肾取肾术的系统评估[J]. 器官移植, 2014, 5(2): 68-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7445.2014.02.003 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 李涛 付生军 董治龙 王志平 王娟 杨立 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 730030 兰州大学泌尿外科研究所 兰州大学第二医院泌尿外科 甘肃省泌尿系统疾病临床医学中心 甘肃省泌尿系统疾病研究重点实验室 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 甘肃省科技支撑计划项目(1011FKCA090) |
| |
| 摘 要: | 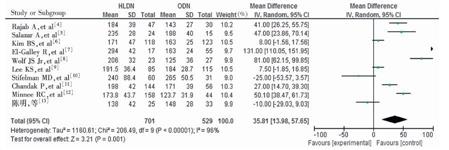
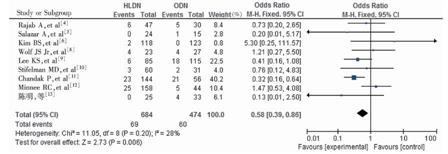
目的 系统评价手助腹腔镜下活体供肾切取术(HLDN)与开放活体供肾切取术(ODN)的安全性及效果。方法 采用计算机互联网检索Pubmed数据库、Sciverse数据库、考克兰图书馆数据库、中国知网、中文科技期刊数据库、中国生物医学文献数据库及万方数据库收录期刊已发表的包含HLDN和ODN两种术式的随机对照试验(RCT)研究。两位研究者根据纳入、排除标准独立筛选文献,应用RevMan 5.2软件进行Meta分析。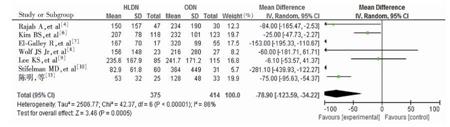
结果 通过筛选共纳入10个RCT,共1 230例患者。Meta分析结果提示,活体供肾取肾时,与ODN术式比较,HLDN术式的手术时间和热缺血时间较长[合并比值比(OR)值为35.81,95%可信区间(CI)13.98~57.65,P=0.001;合并OR 43.99,95% CI 32.31~55.66,P<0.00001],但HLDN术式的术中出血量较少(合并OR-78.90,95% CI -123.59~-34.22,P=0.0005)、并发症发生率较低(合并OR0.58,95%CI0.39~0.86,P=0.006)、住院时间较短[权重均差(WMD)为-1.15,95%CI-1.40~-0.90,P<0.00001];两组患者的术后进普食时间差异无统计学意义(WMD为-0.11,95%CI -0.67~-0.45,P=0.70)。结论 与ODN术式比较,HLDN术式提高了手术的安全性,降低了手术难度,值得临床推广应用。
|
| 关 键 词: | 手助腹腔镜 开放手术 活体供肾取肾术 Meta分析 系统评估 |
| 收稿时间: | 2014-01-07 |
| 本文献已被 CNKI 维普 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《器官移植》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《器官移植》下载全文 |
|



