| [1] Rubin BB, Romaschin A, Walker PM, et al. Mechanisms of postischemic injury in skeletal muscle: intervention strategies . J Appl Physiol (1985).1996;80(2):369-387.
[2] Eckert P, Schnackerz K. Ischemic tolerance of human skeletal muscle. Ann plast surg.1991;26(1):77-84.
[3] Murry CE, Jennings RB, Reimer KA. Preconditioning with ischemia: a delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation.1986;74(5):1124-1136.
[4] Otani H, Kawasaki H, Ninomiya H, et al. Effects of ischemic preconditioning on the recovery of myocardial function after unprotected ischemia and cardioplegia in the isolated and crystalloid perfused rat hearts. Nihon Kyobu Geka Gakkai. 1997;45(1): 23-30.
[5] Zhang Q, Yan S, Tian Y, et al. Ischemic preconditioning improves liver tolerance to congestion-reperfusion injury in mice. J Surg Res.2014;189(1): 152-158.
[6] Cao C, Wang S, Fan L, et al. Renal protection by ischemic preconditioning is associated with p50/p50 homodimers. Am J Nephrol.2010;31(1): 1-8.
[7] Xia DY, Li W, Qian HR, et al. Ischemia preconditioning is neuroprotective in a rat cerebral ischemic injury model through autophagy activation and apoptosis inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2013;46(7): 580-8.
[8] Mallick IH, Yang W, Winslet MC, et al. Protective effects of ischemic preconditioning on the intestinal mucosal microcirculation following ischemia-reperfusion of the intestine. Microcirculation.2005;12(8): 615-25.
[9] Saita Y, Yokoyama K, Nakamura K, et al. Protective effect of ischaemic preconditioning against ischaemia-induced reperfusion injury of skeletal muscle: how many preconditioning cycles are appropriate?. Br J Plast Surg. 2002; 55(3): 241-245.
[10] Mansour Z, Bouitbir J, Charles AL, et al. Remote and local ischemic preconditioning equivalently protects rat skeletal muscle mitochondrial function during experimental aortic cross-clamping. J Vascul surg.2012;55(2): 497-505 e1.
[11] Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, et al. Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2003;285(2): H579-88.
[12] Gulati P, Singh N. Pharmacological evidence for connection of nitric oxide-mediated pathways in neuroprotective mechanism of ischemic postconditioning in mice. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2014;6(4): 233-240.
[13] Young SB, Pires AR, Boaventura GT, et al. Effect of ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning on liver regeneration in prepubertal rats. Transplant Proc. 2014;46(6):1867-1871.
[14] Cao GY, Xie RQ, Cui W, et al. Cardiac protection from myocardial ischemic postconditioning and remote postconditioning during myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rabbits. Zhongguo ying yong sheng li xue za zhi. 2012;28(5): 476-80.
[15] Zhang ZY, Liu XH, Guo XS, et al. Calreticulin is involved in ischemic postconditioning-induced attenuation of ischemia/reperfusion injury in rat skeletal muscle. Sheng li xue bao.2007;59(5): 643-650.
[16] Mcallister SE, Ashrafpour H, Cahoon N, et al. Postconditioning for salvage of ischemic skeletal muscle from reperfusion injury: efficacy and mechanism. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295(2): R681-9.
[17] Yan H, Zhang F, Kochevar AJ, et al. The effect of postconditioning on the muscle flap survival after ischemia- reperfusion injury in rats. J Invest Surg.2010;23(5): 249-256.
[18] Kin H, Zhao ZQ, Sun HY, et al. Postconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting events in the early minutes of reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res.2004;62(1): 74-85.
[19] Iliodromitis EK, Georgiadis M, Cohen MV, et al. Protection from post-conditioning depends on the number of short ischemic insults in anesthetized pigs. Basic research in cardiology. 2006;101(6): 502-507.
[20] Van Vuuren D, Lochner A. Ischaemic postconditioning: from bench to bedside. Cardiovasc J Afr 2008;19(6): 311-320.
[21] Lintz JA, Dalio MB, Joviliano EE, et al. Ischemic pre and postconditioning in skeletal muscle injury produced by ischemia and reperfusion in rats. Acta Cir bras.2013;28(6): 441-446.
[22] Mansour Z, Charles AL, Bouitbir J, et al. Remote and local ischemic postconditioning further impaired skeletal muscle mitochondrial function after ischemia-reperfusion. J Vascul Surg.2012;56(3): 774-82 e1.
[23] Carter WO, Bull C, Bortolon E, et al. A murine skeletal muscle ischemia-reperfusion injury model: differential pathology in BALB/c and DBA/2N mice. J Appl Physiol (1985).1998;85(5): 1676-1683.
[24] Smith JK, Grisham MB, Granger DN, et al. Free radical defense mechanisms and neutrophil infiltration in postischemic skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol.1989;256(3 Pt 2): H789-93.
[25] Park JW, Kang JW, Jeon WJ, et al. Postconditioning protects skeletal muscle from ischemia-reperfusion injury. Microsurgery. 2010;30(3): 223-229.
[26] Zheng W, Huang LZ, Zhao L, et al. Superoxide dismutase activity and malondialdehyde level in plasma and morphological evaluation of acute severe hemorrhagic shock in rats. Am J Emerg Med. 2008;26(1): 54-58.
[27] Hu Y. Experimental study on the role of oxygen-free radicals in ischemic reperfusion tissue injury is island skin flaps . Zhonghua kou qiang yi xue za zhi.1994;29(2): 79-81, 127-128.
[28] Lee KR, Cronenwett JL, Shlafer M, et al. Effect of superoxide dismutase plus catalase on Ca2+ transport in ischemic and reperfused skeletal muscle.J Surg Res.1987; 42(1): 24-32.
[29] Seyama A. The role of oxygen-derived free radicals and the effect of free radical scavengers on skeletal muscle ischemia/reperfusion injury. Surg today.1993;23(12): 1060-1067.
[30] Charles AL, Guilbert AS, Bouitbir J, et al. Effect of postconditioning on mitochondrial dysfunction in experimental aortic cross-clamping. Bri J Surg.2011; 98(4): 511-516. |
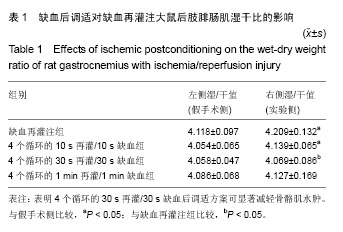
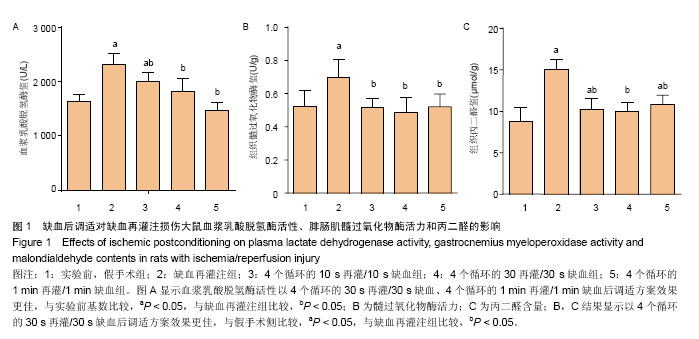

.jpg)