ASRGL1 downregulation suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma tumorigenesis in a CDK1-dependent manner |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Xijing Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, 127 West Changle Street, Xi''an, Shaanxi 710032, China;2. Department of Oncology, Tangdu Hospital, Fourth Military Medical University, Xi''an, Shaanxi 710038, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 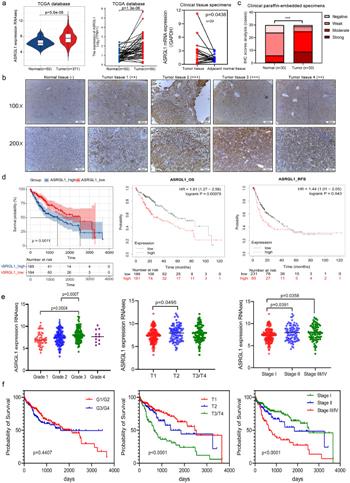
The asparaginase-like protein 1 (ASRGL1) catalyzes the hydrolysis of L-asparagine to L-aspartic acid and ammonia. Emerging evidences have shown a strong correlation between ASRGL1 expression and tumorigenesis. However, the expression and biological function of ASRGL1 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) are still unclear. Here, we explored anti-tumor activity and fundamental mechanisms of ASRGL1 blockade in the HCC progression. Expression levels of ASRGL1 in patients with HCC were higher than those in the adjacent normal tissue. In addition, increased expression of ASRGL1 in HCC patients was correlated with poor overall survival. Knockdown of ASRGL1 gene in HepG2 and Li-7 cell lines inhibited cell proliferation, migration and invasion, but promoted apoptosis in vitro. ASRGL1 knockdown suppressed tumor growth in vivo. Conversely, ASRGL1 overexpression promoted cell proliferation, migration and invasion in HepG2 cells. Through bioinformatics analysis, we found that ASRGL1 might participate in the regulation of the cell cycle. Flow cytometry analysis conformed that ASRGL1 knockdown captured the cell cycle during the G2/M phase. ASRGL1 blockade promoted P53 protein expression and reduced expression of cyclin B and CDK1 proteins, as well as failed to binding. Moreover, CDK1 overexpression was able to reverse the decreased proliferation, migration and invasion of HepG2 cells induced by ASRGL1 knockdown. Collectively, our studies indicate that ASRGL1 blockade functions to inhibit cyclin B/CDK1-dependent cell cycle, leading to G2-to-M phase transition failure and tumor suppression in HCC. |
| |
| Keywords: | ASRGL1" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_INX7VyKMBe" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" asparaginase-like protein 1 HCC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_hEX3Egjady" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" hepatocellular carcinoma CDK" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_EKElEXweJC" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" cyclin-dependent kinase RB1" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_xUa9HLybxQ" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" retinoblastoma 1 PDK1" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_UtlCqhuNhH" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" phosphoinositol dependent protein kinase-1 DMEM" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_A6W2fZO7c4" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" dulbecco's modified eagle medium FBS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_j2yVMaCGSZ" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" fetal bovine serum GFP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_QkO7MhmruK" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" green fluorescent protein OE" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_sOUJym0Ej1" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" overexpression MOI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_c2Ie98XHjd" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" multiplicity of infection CCK8" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_iPhgOVqsol" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" cell counting kit-8 FITC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_gYuxIinoFZ" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" fluorescein isothiocyanate PI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_d9losYqLo0" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" prodium iodide TCGA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_P4slu4GA1I" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" the Cancer Genome Atlas LIHC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_vgXcSGCfxa" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" liver hepatocellular carcinoma DEGs" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_mBvH1Qqb8B" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" differentially expressed genes WGCNA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_I7r97UX3MR" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" weighted gene co-expression network analysis DAVID" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_l8bVXQ1y5K" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery BCA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_auUzS78kst" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" bicinchoninic acid SDS-PAGE" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_TIxsa1yvae" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis PVDF" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_3BnLdgatnQ" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" polyvinylidene fluoride OS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_S5wthJNrIz" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" overall survival RFS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_VmQbg6HWke" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" recurrence-free survival ME" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_OsA9deCs2s" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" module eigengene APC/C" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" pc_ygkazm9PSe" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|
