Protective effects of apocynin nitrone on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Laboratory of Anesthesia and Critical Care Medicine, Translational Neuroscience Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610041, PR China;2. Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan 610041, PR China;3. Department of Anesthesiology, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563000, Guizhou, PR China;4. Laboratory Department, Guizhou Provincial Corps Hospital of PAPF, Guiyang, Guizhou 550000, China;1. Rheumatology Service, Professor Polydoro Ernani São Thiago University Hospital, Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), Campus Universitário, Trindade, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina 88040-970, Brazil;2. Rheumatology Division, Governador Celso Ramos Hospital, Irmã Benwarda street, 297, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina 88015-270, Brazil;3. Department of Clinical Analysis, Center of Health Science, Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), Campus Universitário, Trindade, Florianópolis, Santa Catarina 88040-970, Brazil;1. Department of Clinical Immunology, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland;2. Department of Neurology, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland;3. Department of Histology and Embryology with Experimental Cytology Unit, Medical University of Lublin, Lublin, Poland |
| |
| Abstract: | 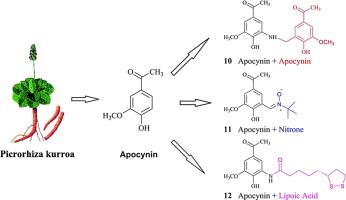
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. In a previous study we reported the synthesis of a series of apocynin derivatives. Although the anti-inflammatory activity of them contributes to these cytoprotective effects. However, the mechanisms and effects of improving LPS-induced ALI in vivo remain unknown, so the purpose of our investigation was designed to reveal the effect of apocynin derivatives on LPS-induced acute lung injury in rats. The present study showed that apocynin derivatives reduces overall protein levels and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) level, inhibits the activation of NADPH oxidase, and increases the levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD). Especially, compound 11 significantly reduces pulmonary vascular permeability, white blood cell content and protein expressions of p67phox and p47phox. These results suggest that compound 11 can ameliorate ALI induced by LPS through inhibition of NADPH oxidase. |
| |
| Keywords: | |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

