Safety,tolerability, and immunogenicity of V114 pneumococcal vaccine compared with PCV13 in a 2+1 regimen in healthy infants: A phase III study (PNEU-PED-EU-2) |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Infectious Diseases, Copenhagen University Hospital, Hvidovre, Denmark;2. Faculty of Medicine and Health Technology, Tampere University, and FVR – Finnish Vaccine Research, Tampere, Finland;3. Department of Woman and Child Health and Public Health, Fondazione Policlinico Universitario Agostino Gemelli IRCCS, Rome, Italy;4. Finnish Vaccine Research, Tampere, Finland;5. The Shraga Segal Department of Microbiology, Immunology and Genetics, Faculty of Health Sciences of the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beer-Sheva, Israel;6. School of Medicine, University of Western Australia, Perth, Australia;7. Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA;8. MSD, Zürich, Switzerland;9. MSD (UK) Limited, London, United Kingdom |
| |
| Abstract: | 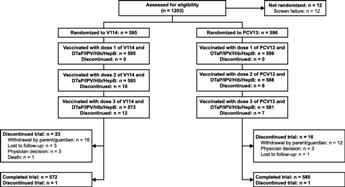
BackgroundThis phase III study evaluated safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of V114 (15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine) in healthy infants. V114 contains all 13 serotypes in PCV13 and additional serotypes 22F and 33F.MethodsHealthy infants were randomized to two primary doses and one toddler dose (2+1 regimen) of V114 or PCV13 at 3, 5, and 12 months of age; diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (DTaP), inactivated poliovirus (IPV), Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), hepatitis B (HepB) vaccine was administered concomitantly. Adverse events (AEs) were collected on Days 1–14 following each vaccination. Serotype-specific anti-pneumococcal immunoglobulin G (IgG) was measured 30 days post-primary series, immediately prior to toddler dose, and 30 days post-toddler dose. Primary objectives included non-inferiority of V114 to PCV13 for 13 shared serotypes and superiority of V114 to PCV13 for serotypes 22F and 33F.Results1191 healthy infants were randomized to V114 (n = 595) or PCV13 (n = 596). Proportions of participants with solicited AEs and serious AEs were comparable between groups. V114 met non-inferiority criteria for 13 shared serotypes, based on difference in proportions with serotype-specific IgG ≥0.35 μg/mL (lower bound of two-sided 95% confidence interval [CI] >−10.0) and IgG geometric mean concentration (GMC) ratios (lower bound of two-sided 95% CI >0.5) at 30 days post-toddler dose. V114 met superiority criteria for serotypes 22F and 33F, based on response rates (lower bound of two-sided 95% CI >10.0) and IgG GMC ratios (lower bound of two-sided 95% CI >2.0) at 30 days post-toddler dose.Antibody responses to DTaP-IPV-Hib-HepB met non-inferiority criteria, based on antigen-specific response rates.ConclusionA two-dose primary series plus toddler dose of V114 was well-tolerated in healthy infants. Compared with PCV13, V114 provided non-inferior immune responses to 13 shared serotypes and superior immune responses to additional serotypes 22F and 33F. |
| |
| Keywords: | Clinical trial Pneumococcal infections Pneumococcal vaccines Child Infant AE" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0035" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" adverse event APaT" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0045" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" all-participants-as-treated CI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0055" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" confidence interval COVID-19" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0065" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" coronavirus disease 2019 CV" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0075" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" coefficient of variation DTaP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0085" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis GMC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0095" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" geometric mean concentration GMT" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0105" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" geometric mean titer HBsAg" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0115" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" HepB surface antigen HepB" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0125" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" hepatitis B Hib" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0135" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," $$" :[{" #name" :" italic" ," _" :" Haemophilus influenzae" },{" #name" :" __text__" ," _" :" type b IgG" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0165" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" immunoglobulin G IgM" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" ce.keyword_rxx_34p_swb" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" immunoglobulin M IPD" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0145" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" invasive pneumococcal disease IPV" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0155" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" inactivated poliovirus mMOPA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0175" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" microcolony multiplexed OPA MMR" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0185" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" measles, mumps, and rubella OPA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0195" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" opsonophagocytic activity PCV" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0205" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" pneumococcal conjugate vaccine PD" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0215" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" pneumococcal disease SAE" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0225" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" serious adverse event WHO" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0235" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" World Health Organization |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

