Comprehensive chemo-profiling of coumarins enriched extract derived from Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa fruit pulp,as an anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory agent |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India, Raj Nagar, Ghaziabad 201002, India;2. Department of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry, Delhi Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research University, New Delhi 110017, India;3. Drugs Controller General of India, Central Drugs Standard Control Organization, FDA Bhawan, Kotla Road, New Delhi 110002, India |
| |
| Abstract: | 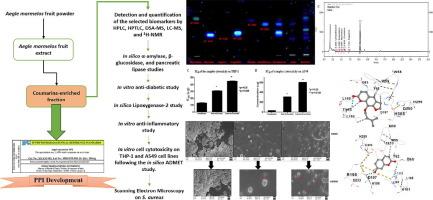
Aegle marmelos (L.) Correa is an Indian medicinal plant known for its vast therapeutic activities. In Ayurveda, the plant is known to balance “vata,” “pitta,” and “kapha” dosh. Recent studies suggest anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial, and anti-diabetic potential but lack in defining the dosage over the therapeutic activities. This study aims to determine the chemical profile of Aegle marmelos fruit extract; identification, enrichment, and characterization of the principal active component(s) having anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic potential. Targeted enrichment of total coumarins, focusing on marmelosin, marmesin, aegeline, psoralen, scopoletin, and umbelliferone, was done from Aegle marmelos fruit pulp, and characterized using advanced high-throughput techniques. In vitro and in silico anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory activities were assessed to confirm their efficacy and affinity as anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory agents. The target compounds were also analysed for toxicity by in silico ADMET study and in vitro MTT assay on THP-1 and A549 cell lines. The coumarins enrichment process designed, was found specific for coumarins isolation as it resulted into 48.61% of total coumarins enrichment, which includes 31.2% marmelosin, 8.9% marmesin, 4% psoralen, 2% scopoletin, 1.7% umbelliferone, and 0.72% aegeline. The quantification with HPTLC and qNMR was found to be correlated with the HPLC assay results. The present study validates the potential use of Aegle marmelos as an anti-inflammatory and anti-diabetic agent. Coumarins enriched from the plant fruit have good therapeutic activity and can be used for Phytopharmaceutical ingredient development. The study is novel, in which coumarins were enriched and characterized by a simple and sophisticated methodology. |
| |
| Keywords: | Bioactive markers enrichment Coumarins qNMR ADMET PPI HPLC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0040" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" High Performance Liquid Chromatography HPTLC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0050" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography LC-MS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0060" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry DSA-MS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0070" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Direct Sample Analysis-Mass Spectrometry SEM" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0080" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Scanning Electron Microscopy MTT" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0090" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide PPI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0100" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Phytopharmaceuticals Ingredient NMR" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0110" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Nuclear Magnetic Resonance BSA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0120" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Bovine Serum Albumin DMSO" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0130" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Dimethyl Sulfoxide VLC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0140" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Vacuum Liquid Chromatography TCA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0150" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Trichloroacetic acid DNS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0160" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" 3,5-Dinitro Salicylic acid THP-1" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0170" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Human Monocytic cell line A549" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0180" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cell line RMPI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0190" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Rosewell Park Memorial Institute DMEM" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0200" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium BSL" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0210" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Biosafety lab FBS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0220" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Foetal Bovine Serum PBS" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0230" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Bovine Serum Albuminn NSAIDs" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0240" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs PPI" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" k0250" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Phytopharmaceutical Ingredients |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

