|
|||||
|
|
| 2010—2019年上海市徐汇区流感样病例流行特征及趋势分析 | |
| 引用本文: | 程凯丽, 曹婧婧, 郑献智, 甄茜, 曹淦, 蒋霞, 吕旭峰. 2019—2023年江苏省常州市流行性感冒流行特征分析[J]. 上海预防医学, 2023, 35(11): 1063-1067. DOI: 10.19428/j.cnki.sjpm.2023.23157 |
| 作者姓名: | 程凯丽 曹婧婧 郑献智 甄茜 曹淦 蒋霞 吕旭峰 |
| 作者单位: | 1.南京医科大学,江苏 南京 211100;2.常州市疾病预防控制中心,江苏 常州 213002 |
| 基金项目: | 江苏省常州市社会发展支撑项目(CE20205032);常州市科技局应用基础研究项目(CJ20200031) |
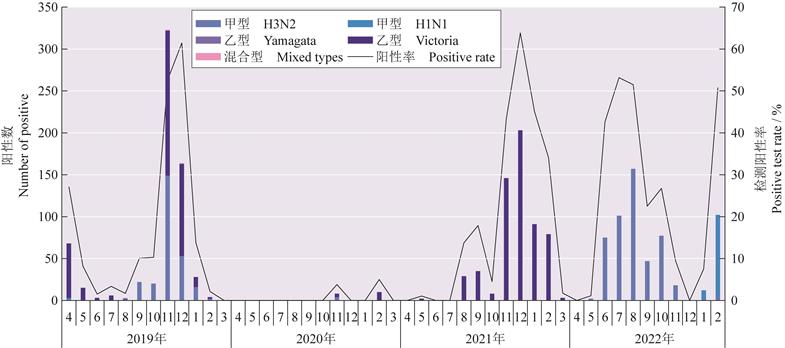
| 摘 要: | 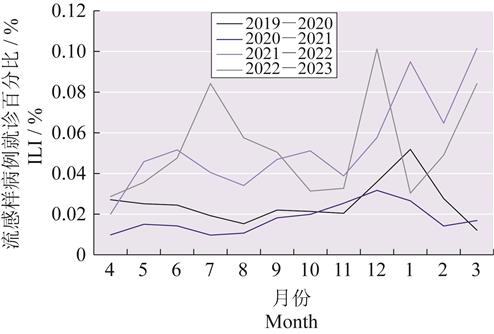 分析2019—2023年江苏省常州市流行性感冒(简称“流感”)的流行强度和特征,为制订流感防控策略提供科学依据。 通过中国流感监测信息系统收集常州市2019年4月—2023年3月流感监测哨点医院的监测数据,对常州市新型冠状病毒感染(简称“新冠”)流行前后的流感样病例(ILI)进行分析研究,采用 常州市2019年4月—2023年3月的ILI就诊百分比分别为2.57%、1.84%、5.38%、3.66%,流感病毒阳性检出率分别为25.71%、0.44%、22.78%、24.32%,流感暴发疫情数分别为61起、1起、23起和128起。ILI主要以5~14岁的青少年和儿童为主。2020—2021年新冠流行后ILI就诊百分比明显低于2019—2020年( 2019—2023年新冠防控不同阶段流感的流行特征不同,在新冠疫情动态清零阶段,ILI就诊呈现低水平波动,无明显季节性波动,且流感病毒阳性检出以乙型为主;新冠高强度流行阶段,ILI就诊水平达到历年高峰,流感病毒阳性检出以甲型H3N2型为主;新冠乙类乙管阶段,ILI就诊水平在迅速降低后升高,流感病毒阳性检出以甲型H1N1型为主。须进一步加强对流感病例的监测,密切关注流感毒株变化,积极推进重点人群流感疫苗接种,促进全人群健康行为改变。  |
| 关 键 词: | 流行性感冒 新型冠状病毒感染 流感样病例 防控措施 |
| 收稿时间: | 2023-04-28 |
| 点击此处可从《上海预防医学》浏览原始摘要信息 | |
| 点击此处可从《上海预防医学》下载全文 | |