Okra polysaccharide-2 plays a vital role on the activation of RAW264.7 cells by TLR2/4-mediated signal transduction pathways |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Natural Constituents Research Center, Institute of Natural Products, Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), Gangneung, 210-340, Republic of Korea;2. Department of Food Science and Biotechnology, Kyonggi University, San 94-6, Ieui-dong, Youngtong-gu, Suwon, Gyeonggi-do 443-760, Republic of Korea;3. Korea Food Research Institute, Seongnam, Gyeonggi-do 463-836, Republic of Korea |
| |
| Abstract: | 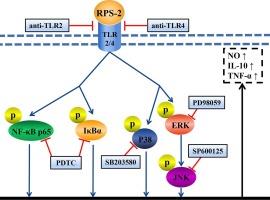
Polysaccharide is the main active component of okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.) and it can effectively stimulate the activation of macrophages. However, the immune regulatory mechanism is still not clear. Therefore, the present study aimed to reveal the possible mechanism by investigating the effect of okra polysaccharide-2 (RPS-2) on Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2/4-mediated signal transduction pathways in RAW264.7 murine macrophage cells. In order to confirm whether RPS-2 stimulated macrophages activation via TLR2 or TLR4, RAW264.7 murine macrophage cells were pretreated with TLR2/4 inhibitors for 1 h before RPS-2 treatment, and then the NO, IL-10, TNF-α levels were tested. The results indicated that both TLR2 and TLR4 were the keys of immune regulatory effect of RPS-2. Afterwards, the effect of RPS-2 on NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways were studied by western blot analysis. It showed RPS-2 induced the phosphorylation of p65, IκBα, p38, ERK1/2 and JNK. At the same time, the specific inhibitors reduced these phosphorylation levels as well as NO, IL-10 and TNF-α amounts. In a word, RPS-2 activated macrophages by NF-κB and MAPKs signal transduction pathways. |
| |
| Keywords: | Okra polysaccharide-2 Toll-like receptor NF-κB MAPKs |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

