The clinical and immunological significance of GAD-specific autoantibody and T-cell responses in type 1 diabetes |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Type 1 Diabetes Center, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, 9420 Athena Circle, La Jolla, CA 92037, United States;2. Diamyd Medical AB, Karlavägen 108, SE-115 26, Stockholm, Sweden |
| |
| Abstract: | 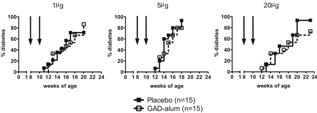
Antigen-specific interventions are desirable approaches in Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) as they can alter islet-specific autoimmunity without systemic side effects. Glutamic acid decarboxylase of 65 kDa (GAD65) is a major autoantigen in type 1 diabetes (T1D) and GAD-specific autoimmunity is a common feature of T1D in humans but also in mouse models of the disease. In humans, administration of the GAD65 protein in an alum formulation has been shown to reduce C-peptide decline in recently diagnosed patients, however, these observations were not confirmed in subsequent phase II/III clinical trials. As GAD-based immune interventions in different formulations have successfully been employed to prevent the establishment of T1D in mouse models of T1D, we sought to analyze the efficacy of GAD-alum treatment and the effects on the GAD-specific immune response in two different mouse models of T1D. Consistent with the latest clinical trials, mice treated with GAD-alum were not protected from diabetes, although GAD-alum induced a GAD-specific Th2-deviated immune response in transgenic rat insulin promoter-glycoprotein (RIP-GP) mice. These observations underline the importance of a thorough, preclinical evaluation of potential drugs before the initiation of clinical trials. |
| |
| Keywords: | Type 1 diabetes GAD65 GAD-alum Immunotherapy NOD RIP-LCMV GAD65" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0045" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" Glutamic acid decarboxylase of 65 kDa T1D" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0055" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" type 1 diabetes NOD" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0065" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" non-obese diabetic LCMV" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0075" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus RIP-GP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0085" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" rat insulin promoter-glycoprotein TNF" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0095" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" tumor necrosis factor IFN-γ" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0105" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" interferon-γ PBMC" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0115" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" peripheral blood mononuclear cells IL" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0125" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" interleukin Th" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0135" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" T-helper PFU" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0145" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" plaque-forming units GABA" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0155" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" γ-aminobutyric acid |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

