| 鸡蛋摄入与非酒精性脂肪肝病患病风险的病例对照研究 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 陈冰冰, 李慧泉, 潘欣婷, 李扬帆, 刘文娟, 闫建慧, 徐尚华, 彭仙娥. 鸡蛋摄入与非酒精性脂肪肝病患病风险的病例对照研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2020, 24(7): 767-772. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2020.07.005 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 陈冰冰 李慧泉 潘欣婷 李扬帆 刘文娟 闫建慧 徐尚华 彭仙娥 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.350000 福州, 福建医科大学公共卫生学院流行病与卫生统计学系;;2.350000 福州, 福建省疾病预防控制中心;;3.350000 福州, 福建省儿童医院;;4.570100 海口, 海南医学院第二附属医院院感科;;5.353000 南平, 南平市第一医院 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 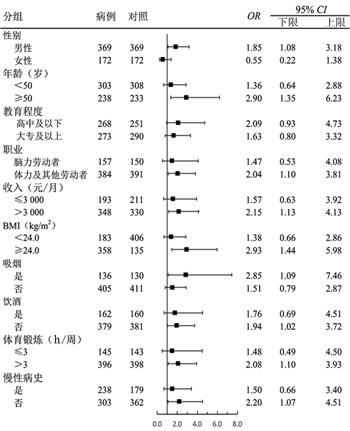
目的 探讨鸡蛋摄入与非酒精性脂肪肝病(non-alcoholic fatty liver disease,NAFLD)患病风险的关系,为NAFLD的防控提供流行病学依据。 方法 收集2015年4月―2017年8月在南平市第一医院体检中心进行健康检查的体检者数据,以腹部彩超确诊的541名病例和按年龄性别随机抽取的541名对照进行病例对照研究。采用统一编制的结构式调查问卷及半定量食物频数问卷面对面调查研究对象的一般行为特征及膳食摄入情况。多因素非条件Logistic回归分析模型计算OR值及其95%CI,探索鸡蛋摄入与NAFLD患病风险的关系。 结果 与每天摄入鸡蛋相比,鸡蛋摄入频率为0患NAFLD的风险增高,其调整的OR值及其95% CI为1.86(95% CI:1.10~3.15)。敏感分析结果及亚组分析均显示从不摄入鸡蛋仍然是NAFLD的危险因素。 结论 从不摄入鸡蛋可能增高NAFLD的患病风险。
|
| 关 键 词: | 鸡蛋摄入 非酒精性脂肪肝病 病例对照研究 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-12-15 |
| 修稿时间: | 2020-01-07 |
| 本文献已被 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《中华疾病控制杂志》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中华疾病控制杂志》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|

