| 中国母婴健康相关队列研究的文献计量分析 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 刘璇, 黄萍, 湛永乐, 陈云利, 石英杰, 岳和欣, 景傲, 孟耀涵, 吕天琛, 张一方, 曲翌敏, 黎小秀, 江宇. 中国母婴健康相关队列研究的文献计量分析[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2021, 25(2): 155-159. doi: 10.16462/j.cnki.zhjbkz.2021.02.007 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 刘璇 黄萍 湛永乐 陈云利 石英杰 岳和欣 景傲 孟耀涵 吕天琛 张一方 曲翌敏 黎小秀 江宇 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.100730 北京,中国医学科学院/北京协和医学院群医学及公共卫生学院流行病与生物统计学系;;2.330006 南昌,南昌大学第一附属医院营养科;;3.523000 东莞,东莞市妇幼保健院儿科 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 中国医学科学院医学与健康科技创新工程(2019-I2M-2-007)。 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 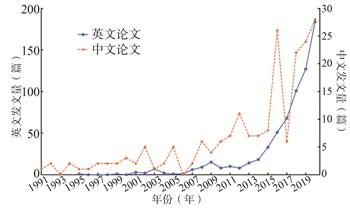
目的 回顾分析母婴健康队列研究的应用趋势,展望未来发展方向。 方法 检索中国发表的中文及英文(简称“中英文”)母婴队列研究文献,对发表时间、科研单位、研究目标与随访调查等情况进行统计分析。 结果 自1991年以来,母婴健康队列研究的文献数量明显增加,中英文核心期刊群均已形成。中英文文献发表数量的年平均增长率分别为12.2%和23.2%,54.4%的中文文献与79.3%的英文文献为近5年发表。56.9%的中文文献发表在核心期刊,54.3%的英文文献发表在影响因子>3分的期刊。国内外期刊发表的文献均以病因研究为主,多为大样本研究,回归分析模型运用普遍。 结论 队列研究在我国母婴健康领域的应用逐渐增加,但研究者仍需加强对队列研究的认识,控制失访率、改善随访效果,运用Cox回归分析模型等统计分析方法,更加科学地运用队列研究解决实际问题。
|
| 关 键 词: | 母婴健康 队列研究 流行病学 文献计量学 |
| 收稿时间: | 2020-12-30 |
| 修稿时间: | 2021-01-07 |
| 本文献已被 维普 万方数据 等数据库收录! |
| 点击此处可从《中华疾病控制杂志》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中华疾病控制杂志》下载免费的PDF全文 |
|

