Determination and health risk assessment of heavy metals in imported rice bran oil in Iran |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Environmental Health Engineering, Division in Food Safety and Hygiene, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;2. Student’s Scientific Research Center, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;3. Department of Environmental Health Engineering, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;4. Department of Environmental Health Engineering, School of Public Health, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran;5. DVM, MPh, PhD in Nutrition Science, National Nutrition & Food Technology Research Institute (NNFTRI), Director of Research & Education Affairs Office of International Affairs, The Member of Food Safety Research Center Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;1. Center for Air Pollution Research (CAPR), Institute for Environmental Research (IER), Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;2. Department of Environmental Health Engineering, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran;3. Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA;4. Department of Hydrology and Atmospheric Sciences, University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA;5. Department of Occupational Health Engineering, School of Public Health, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran;6. Department of Remote Sensing & GIS, Faculty of Geography, University of Tehran, Tehran, Iran;7. Department of Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Shahroud University of Medical Sciences, Shahroud, Iran;1. Institute of Apicultural Research, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100093, China;2. Laboratory of Risk Assessment for Quality and Safety of Bee Products, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100093, China;3. Key Laboratory of Bee Products for Quality and Safety Control, Ministry of Agriculture, Beijing 100093, China;4. Wuhan Institute of Physics and Mathematics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, National Center for Magnetic Resonance in Wuhan, Wuhan 430071, China;5. Department of Analytical Chemistry, Applied Chemometrics and Molecular Modelling, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Laarbeeklaan 103, B-1090 Brussels, Belgium;6. National Isotope Center, GNS Science, 30 Gracefield Road, Lower Hutt 5040, New Zealand;1. Department of Computer Science, University of Oviedo, Campus de Gijón s/n, 33203 Gijón, Spain;2. Nutrition Research Programme, Regional Service for Agri-food Research and Development (SERIDA), PO Box 13, 33300 Villaviciosa, Spain |
| |
| Abstract: | 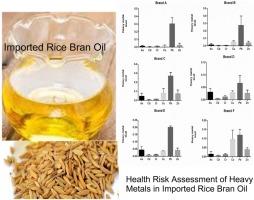
In this current study, the contents of heavy metals including Pb, As, Cr, Cd, Zn, Cu, and Mn in imported rice bran oil in Iran were investigated with microwave digestion method based on an inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry system (ICP-OES). The concentrations range of Pb, Cr, Cd, As, Zn, and Cu in rice bran oil samples were measured as 0.066–0.30, 0.008–0.014, 0.005–0.01, 0.047–0.01, 0.025–0.74 and 0.01–0.096 μg/g, respectively. A significant difference (p-value < 0.05) in the mean concentration of Pb in imported rice bran oils samples was observed. The sum of incremental lifetime cancer risk (ILCR) for heavy metals for children and adults were 2.6 × 10−4 and 2.4 × 10−5, respectively, which an acceptable level proposed values (10−4–10−6) by U.S. EPA. Moreover, the target hazard quotients (THQs) of As, Pb, Cr, Cd, Cu, and Zn for children were limited to between 1.17 × 10-5 and 9.49 × 10−9, and in adults were limited to 2.33 × 10−7and 6.82 × 10-7, which were lower than the acceptable limit (THQ < 1). There have been concerns regarding heavy metals since past up to now in all foodstuffs. We demonstrated in this study that there are traceable concentrations of heavy metals in six brand of rice bran oils. |
| |
| Keywords: | Rice bran oil Heavy metal Risk assessment Hazard quotient Food analysis Food composition |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

