Nutrient composition of 19 fish species from Sri Lanka and potential contribution to food and nutrition security |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Institute of Marine Research, P.O. Box 2029 Nordnes, 5817 Bergen, Norway;2. Institute of Postharvest Technology, National Aquatic Resources Research and Development Agency, Colombo, Sri Lanka;3. WorldFish, Jalan Batu Muang, Batu Muang, Bayan Lepas, 11960 Penang, Malaysia;4. Health and Nutrition, Social Assistance and Rehabilitation for the Physically Vulnerable (SARPV), Cox’s Bazar, Bangladesh;5. Marine Fisheries Survey Management Unit, Department of Fisheries, Bangladesh;6. Wildlife Conservation Society-Myanmar Program, P.O. Box Kamayut, 11041 Yangon, Myanmar |
| |
| Abstract: | 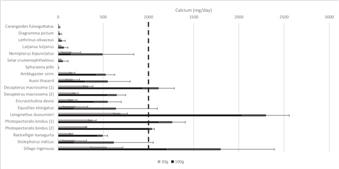
Fish is an important part of the Sri Lankan diet. However, existing data on the nutrient composition of fish in Sri Lanka is highly outdated and limited. The aim of this study was to report the nutrient composition of commonly consumed marine fish species in Sri Lanka and assess the potential contribution of selected key nutrients in fish to recommended nutrient intakes (RNI). Fish were sampled during a survey with research vessel Dr. Fridtjof Nansen around Sri Lanka. Species were categorised as either small (<25 cm, n = 12) or large (>25 cm, n = 7), and three composite samples from each species were analysed using accredited methods. Small species commonly consumed whole contained significantly higher concentrations of micronutrients such as calcium (960 mg/100 g), iron (3.3 mg/100 g), zinc (2.1 mg/100 g), vitamin A (295 μg/100 g), and EPA and DHA (0.14 and 0.32 g/100 g, respectively) than larger species where only the fillet is consumed. Several species were identified to contribute ≥25 % of the RNI of women of reproductive age for multiple essential nutrients. These data may represent an important contribution to the future development of the Sri Lankan food composition database. |
| |
| Keywords: | Food composition Fish Marine Food analysis Sri Lanka Nutrients Minerals Micronutrients Food and nutrition security Recommended nutrient intakes |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

