The ameliorating effects of selenium and vitamin C against fenitrothion-induced blood toxicity in Wistar rats |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Department of Zoology, Faculty of Biology and Environmental Protection, University of Silesia in Katowice, Bankowa 9, 40-007 Katowice, Poland;2. National Insect Museum, National Agricultural Research Centre NARC, Islamabad, Pakistan |
| |
| Abstract: | 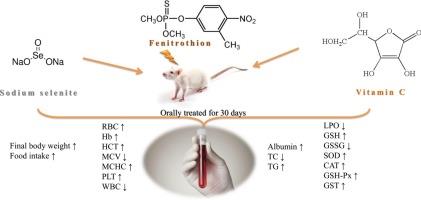
Fenitrothion is widely used organophosphate pesticide in agriculture and health programs, but besides, it causes several toxic effects. The present study was designed to evaluate the possible protective effects of selenium (0.5 mg/kg b.w.) and vitamin C (100 mg/kg b.w) on altered haematological, biochemical and oxidative stress parameters in the blood of rats orally treated with fenitrothion (20 mg/kg b.w) for 30 days. Fenitrothion caused changes in body weight, food and water intake, and some haematological and biochemical parameters. Fenitrothion altered the glutathione redox status (GSH and GSSG) and decreased activity of antioxidant enzymes (GSH-Px, GST, SOD and CAT), leading to a lipid peroxidation. Selenium and vitamin C, by improving the activity of antioxidants, reduced oxidative stress and a lipid peroxidation, maintaining the values of examined parameters to optimal levels. Therefore, selenium and vitamin C could be useful in providing protection of exposed non-target organisms including people from fenitrothion. |
| |
| Keywords: | Fenitrothion Selenium Vitamin C Oxidative stress Antioxidative defence |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

