Crocin attenuates hemorrhagic shock-induced oxidative stress and organ injuries in rats |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. College of Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Zhejiang University of Technology, No. 6 District, Zhaohui, Hangzhou 310032, China;2. School of Advanced Study, Taizhou University, Taizhou 318000, China |
| |
| Abstract: | 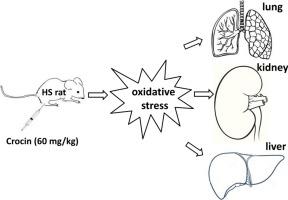
We aimed to evaluate the effect of natural antioxidant crocin in alleviating hemorrhagic shock (HS)-induced organ damages. HS rats were treated with crocin during resuscitation. Mortality at 12 h and 24 h post resuscitation was documented. HS and resuscitation induced organ injuries, as characterized by elevated wet/dry ratio, quantitative assessment ratio, blood urea nitrogen, creatinine, aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase, whereas rats received crocin treatment demonstrated improvements in all the above characteristics. This protective effect coincided with reduced malondialdehyde and increased glutathione in both serum and lung tissues, indicating attenuated oxidative stress in crocin-treated rats. Myeloperoxide levels in lung, kidney and liver were also reduced. Crocin can potentially be used to protect organs from HS-induced damages during resuscitation due to its anti-oxidative role. |
| |
| Keywords: | Crocin Hemorrhagic shock Oxidative stress Organ injury |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

