Beta-cell specific production of IL6 in conjunction with a mainly intracellular but not mainly surface viral protein causes diabetes |
| |
| Affiliation: | 1. Type 1 Diabetes Center, La Jolla Institute for Allergy and Immunology, 9420 Athena Circle, La Jolla, CA 92037, USA;2. The School of Molecular Bioscience, University of Sydney, NSW 2006, Australia |
| |
| Abstract: | 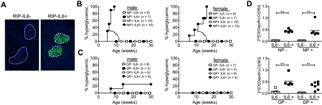
Inflammatory mechanisms play a key role in the pathogenesis of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. IL6, a pleiotropic cytokine with impact on immune and non-immune cell types, has been proposed to be involved in the events causing both forms of diabetes and to play a key role in experimental insulin-dependent diabetes development. The aim of this study was to investigate how beta-cell specific overexpression of IL-6 influences diabetes development. We developed two lines of rat insulin promoter (RIP)-lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) mice that also co-express IL6 in their beta-cells. Expression of the viral nucleoprotein (NP), which has a predominantly intracellular localization, together with IL6 led to hyperglycemia, which was associated with a loss of GLUT-2 expression in the pancreatic beta-cells and infiltration of CD11b+ cells, but not T cells, in the pancreas. In contrast, overexpression of the LCMV glycoprotein (GP), which can localize to the surface, with IL-6 did not lead to spontaneous diabetes, but accelerated virus-induced diabetes by increasing autoantigen-specific CD8+ T cell responses and reducing the regulatory T cell fraction, leading to increased pancreatic infiltration by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells as well as CD11b+ and CD11c+ cells. The production of IL-6 in beta-cells acts prodiabetic, underscoring the potential benefit of targeting IL6 in diabetes. |
| |
| Keywords: | Type 1 diabetes Cytokine GLUT-2 Inflammation T cell T1D" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0060" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" type 1 diabetes IDDM" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0070" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus NOD" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0080" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" non-obese diabetic LCMV" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0090" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus RIP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0100" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" rat insulin promoter GP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0110" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" glycoprotein NP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0120" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" nucleoprotein Tg" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0130" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" transgenic IL" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0140" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" interleukin TNF" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0150" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" tumor necrosis factor IFN-γ" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0160" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" interferon-γ Th" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0170" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" T-helper PFU" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0180" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" plaque-forming units GLUT-2" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0190" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" glucose transporter 2 XBP-1" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0200" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" X-box binding protein-1 CHOP" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0210" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" C/EBP homologous protein ER" },{" #name" :" keyword" ," $" :{" id" :" kwrd0220" }," $$" :[{" #name" :" text" ," _" :" endoplasmic reticulum |
| 本文献已被 ScienceDirect 等数据库收录! |
|

