| 初级卫生保健试点县妇幼保健投入产出分析 |
| |
| 引用本文: | 马东平, 尹文强, 田壮, 郑文贵, 马安宁, 林振平, 钱东福, 李程跃, 尹爱田, 郝模. 京沪妇女保健财力资源适宜程度分析[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2020, 36(10): 1471-1473. DOI: 10.11847/zgggws1122674 |
| |
| 作者姓名: | 马东平 尹文强 田壮 郑文贵 马安宁 林振平 钱东福 李程跃 尹爱田 郝模 |
| |
| 作者单位: | 1.潍坊医学院公共卫生与管理学院,潍坊 261053;2.“健康山东”重大社会风险预测与治理协同创新中心;3.健康相关重大社会风险预警协同创新中心;4.济宁医学院公共卫生学院;5.南京医科大学医政学院;6.复旦大学卫生发展战略研究中心;7.山东大学医药卫生管理学院 |
| |
| 基金项目: | 上海市加强公共卫生体系建设三年行动计划(2015 — 2017年,GWIV – 32);潍坊医学院科技创新团队支持计划(201701);“健康山东”重大社会风险预测与治理协同创新中心重点研究方向项目(XT1407004);潍坊医学院博士科研启动基金(02177801);潍坊医学院公派教师国内访学项目 |
| |
| 摘 要: | 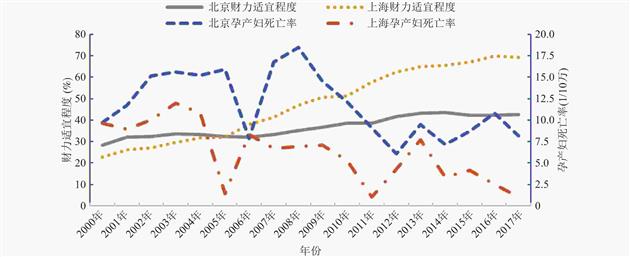
目的 分析2000 — 2017年京沪妇女保健财力资源适宜程度及孕产妇死亡率的变化趋势,明确2地差异,探讨妇女保健财力资源适宜程度。 方法 收集1995 — 2017年涉及京沪妇女保健财力投入政府主导问题(202篇)、投入总量问题(205篇)和投入增长问题(122篇)文献,综合投入政府主导适宜程度、投入总量适宜程度、增长适宜程度等3个指标,计算财力资源的适宜程度。运用Spearman相关、线性回归等分析妇女保健财力资源适宜程度与孕产妇死亡率的关系。 结果 北京妇女保健财力资源适宜程度从2000年的28.40 %升至2017年的42.60 %,上海则由22.60 %升至69.40 %,北京和上海的回归方程均有统计学意义(上海P < 0.01,北京P < 0.05)。 结论 京沪2地妇女保健财力资源适宜程度逐年提高,上海财力资源在孕产妇死亡率下降中作用更大,但财力投入稳定增长仍是薄弱环节;适宜的妇女保健体系应“政府负责、投入适宜、稳定增长”;验证了量化妇女保健财力资源适宜程度的可行性。
|
| 关 键 词: | 妇女保健 财力资源 适宜程度 北京 上海 |
| 收稿时间: | 2019-01-07 |
|
| 点击此处可从《中国公共卫生》浏览原始摘要信息 |
|
点击此处可从《中国公共卫生》下载全文 |
|

